SQL data manipulation language (DML)
- SELECT, FROM, WHERE
- NULL values
- Set operations
- String operations, ordering
- Aggregate functions, aggregation
→ querying && modifying the databases
Aggregate Functions - Having Clause
- groups뒤에 오는 HAVING과 groups 앞에 있는 HAVING이 다름.

- 두 개는 다른 쿼리이다.
- 왼쪽에 있는 것은 GROUP BY 를 한 instructor중에서 65000이 넘는 교수
- 오른쪽은 65000이 넘는 instructor를 찾아서 평균을 낸 것. 따라서 더 높음.
More SQL
- Nested subqueries
- 쿼리를 다른 쿼리에 더하는 것
- Set Membership(SOME, ALL, EXISTS)
- Modification of databases
- (insert, update, delete)
Nested Subqueries
- SQL provides a mechanism for the nesting of subquery
- A subquery is a SELECT-FROM-WHERE expression
- nested within another query
- 하나의 쿼리를 다른 쿼리에 put하는 것.
- SELECT A1, A2, ... , An
- FROM r1, r2, ..., rm
- WHERE P
- FROM clause
- ri can be replaces by any valid subquery
- 아무거나 올 수 있음.
- WHERE clause
- P can be replaced with an expression of the form
- B <operation> (subquery)
- SELECT clause
- Ai can be replaced be a subquery that generates a single value
- scalar subquery
- 특정 column을 선택 → multiple attribute in one time. limitation 이 있음.
- FROM clause
WITH Clause
- variables를 정의
- provides a way of defining a temporary relation
- the relation is available only to the query in which the WITH clause occurs
Scalar Subquery
- used where a single value is expected
- runtime error occurs if a subquery returns more than one result tuple
- scalar value와 single value는 같다.
- SELECT 쿼리에서 필요로 함.
Set membership(SOME, ALL, EXISTS)
Interpretation of SOME

- (=SOME) 은 IN과 같다.
- 그러나, ≠SOME은 NOT IN 과 같지 않다.
- ≠SOME은 몇몇이 아닌, 하나라도 가지고 있지 않은게 있으면 참이지만, NOT IN은 아무것도 없어야 참이 된다.
Interpretation of ALL
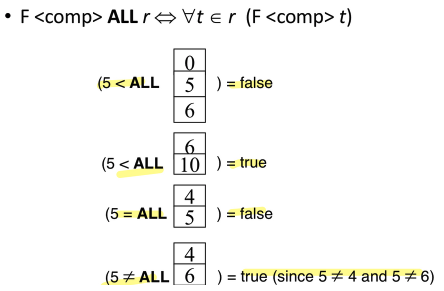
- (≠ALL) 은 NOT IN 과 같지 않다.
- 그러나, (=ALL)은 IN이 아니다.
- (=ALL)은 모두를 가리키고, IN은 적어도 하나가 포함되어 있으면 참이 된다.
Test for Empty Relations
- EXIST
- returns the value true if the argument subquery is nonempty
- 비어 있지 않으면 true를 리턴.
- NOT EXIST
- 아무것도 없으면 true를 리턴.
Test for Absence of Duplicate Tuples
- UNIQUE(MySQL X)
- construct tests whether a subquery has any duplicate tuples in its result
- UNIQUE
- "true" → if given subquery contains no duplicates
- UNIQUE
- construct tests whether a subquery has any duplicate tuples in its result
IN, NOT IN vs EXISTS, NOT EXISTS
- IN, NOT IN
- set이 주어지고, 여기에 들어가는 조건을 만족하면 in이 된다.
- EXISTS, NOT EXISTS
- 계산하고 남은 relational 이 empty냐 아니냐에 관한 부분.
Modification of database
SQL Commands
- SQL
- DML - SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- Data Manipulation
- these change the data content but are not changing the data schema
- DDL - CREATE, ALTER, DROP
- change table structure
INSERT
- Basic syntax
- insert data in to every column
- INSERT INTO tablename VALUES (col1_value, col2_value, ...)→ # attributes type of attribute values
- → Assumption; one is provided and know the table schema
- Must list values in the same order as in the table schema
- If some data values are unknown, must type NULL
- place order!!!
- For character sequences, use quotation marks
- Single quotation marks을 추천 → double도 가능.
- Value in quotation is case-sensitive
- ADD a new tuple to course
INSERT INTO course
VALUES ('CS-437', 'Database Systems', 'Comp.Sci', 4);
INSERT INTO course(course_id, title, dept_name, credits)
VALUES ('CS-437', 'Database Systems', 'Comp.Sci', 4);
// ADD a new tuple student with tot_creds set to null
INSERT INTO student
VALUES('3003', 'GREEN', 'Finance', null);
Foreign key
- specifies that an attribute from one relation has to map a tuple in another relation
- Values in one relation must appear in another relation
- is referencing PK in another table any value in FK has to exist in the referenced PK
- PK; identifies the records in a table, has to be unique
- Make sure all foreign keys that new row references have already been added to database
- One cannot insert a foreign key value unless the corresponding value exists in the referenced relation
- PK에 없는 것을 FK에 담을 수 없다.
- DBMS rejects this as there is no "martial arts" in PK

- Add to department table
- Add to instance table
- The SELECT FROM WHERE statement is evaluated fully before any of its results are inserted into the relation
- Otherwise queries like
- INSERT INTO table1 SELECT * FROM table1
- would cause problem
- Otherwise queries like
- DML does NOT change the data schema.
UPDATE
- updating a table
UPDATE tablename
SET col1_name = new_col1_value, col1_name = new_col1_value, ... ; //specify only the columns that you want to update
UPDATE tablename
SET col1_name = new_col1_value, co1_name = new_col1_value, ...
WHERE predicate //조건절
CASE Statement for Conditional Update
UPDATE instructor
SET salary = CASE
WHEN salary <= 100000 THEN salary * 1.05
ELSE salary * 1.03
END
- conditional block
DELETE
DELETE FROM tablename
WHERE predicate;
<=>
TRUNCATE(TABLE) tablename;
- remove specific rows
- 전체를 지우고 싶을 때, this doesn't mean you are removing the table structure
- One cannot truncate a table with foreign key constraints
- referential integrity
- FK가 있는 것은 지울 수 없다.
- Must disable the constraints first
- ALTER
ALTER TABLE tablename
DISABLE CONSTRAINT constraint_name;
SQL data definition language (DDL)
Data Definition Language
- allows the specification of information about relations,
- schema; for each relation
- table structure = schema
- type; associated with each attribute
- constraints; integrity constraints
- indices; set of indices to be maintained for each relation
- Security and authorization information for each relation
- index를 설정하는 것.
- physical storage structure of each relation on disk
- schema; for each relation
- CREATE, ALTER, DROP
c.f SQL DML
- manipulate data
- does NOT change the table structure
- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT
Domain Types in SQL
SQL Data Types
- CHAR(n)
- Fixed length character string
- with user-specified length n
- Maximum length n = [0, 255]
- VARCHAR(n)
- Variable length character strings
- user-specified maximum length n
- Maximum length n = [0, 65, 535]
- TEXT
- for strings longer than the range of VARCHAR
- TINYTEXT: 0-255 bytes
- TEXT: 0-65,535 bytes
- MEDIUMTEXT: 0-16,777,215 bytes
- LONGTEXT: 0-4,294,967,296 bytes
- for strings longer than the range of VARCHAR
Different between CHAR and VARCHAR
- **CHAR는 무조건 4byte로 고정,
- for each record allows allocatte 4 bytes regardless of the data value
- **VARCHAR는 +1 bytes로 들어간다. 0/ 이게 하나씩 들어가기 때문
- for each records, allocate up to 4 + 1(end of string character) bytes
- INT, INTEGERR
- integer
- a finite subset of the integers that is machine-dependent
- SMALLINT
- small integer
- a machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type
- BIGINT
- Big integer
- a machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type
- TINYINT
- MEDIUMINT
- → ORACLE은 INT가 없고, NUMBER로만 가능하다.
- NUMERIC(p,d)
- fixed point number (exact value)
- user-specified precision of p digits
- p; 총 자릿수
- with d digits to the right of decimal point
- d; 소수점 자릿수
- MySQL에서 DECIMAL은 NUMERIC하다.
- FLOAT
- Floating point number
- single-precision
- REAL, DOUBLE
- Floating point number
- double-precision
- FLOAT, DOUBLE >> DECIMAL (faster)
- DECIMAL; exact
- float은 1.1+1.1+1.1=3..3000000715255737이러는데 decimal은 3.30 그대로 나온다.
- DATE
- 'YYYY-MM-DD'
- 1000-01-01 to 9999-12-31
- TIME
- HH:MM:SS
- Range: -839:59:59 ~ 839:59:59
- 14:30:03.5 → 3.5 seconds after 2:30pm
- DATETIME
- YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
- Range: 1000-01-01 00:00:00 ~ 9999-12-31 23:59:59
- YEAR
- YYYY
- 1901 ~ 2155 or 0000
- illegal year values are converted to 0000
- TIMESTAMP
- Unix time
- Range: 1970-01-01 00:00:01 UTC ~ 2038-01-19 03:14:07 UTC
- Typically used for logging (keep records of all the systems events)
- Depending on size n, the display pattern changes
- long type variable이 아니라 int(SQL) → 4 bytes in SQL임.
- in terms of storage; same amount of space를 갖는다.

- BINARY(n)
- binary byte data type
- user-specified length n
- contains a byte strings (rather than a character string)
- Maximum length n = [0, 255]
- VARBINARY(n)
- binary byte data type
- user-specified maximum length n
- Maximum length n = [0, 65, 535]
- BLOB
- Binary Large OBject data type
- TINYBLOB; 0-255 bytes
- BLOB; 0 - 65,535 bytes (65 KB)
- MEDIUMBLOB; 0 - 16,777,215 bytes (16 MB)
- LONGBLOB; 0 - 4,294,967,295 bytes (4 GB)
CREATE TABLE Construct
- CREATE TABLE r
- r is the name of the relation
- Each Ai is an attribute name in the schema of relation r
- Each Di is the data type of values in the domain of attribute Ai
CREATE TABLE instructor(
ID CHAR(5),
name VARCHAR(20),
dept_name VARCHAR(20),
salary NUMERIC(8,2)
)
- After creating a database, to use it
- USE database_name
Integrity Constraints in CREATE TABLE
- SQL prevents any update to the database that violates an integrity constraints
- integrity constraints allow us to specify what data makes sense for us
- Types of integrity constraints
- PRIMARY KEY (A1, ... , An)
- a column representing each records in a table
- a combination of columns can form a PK
- 하나의 테이블에 여러가지 CK가 있고, 그 중에 하나가 PK임.
- FOREIGN KEY (A1, ... , Am) REFERENCES r
- UNIQUE
- PK와 비슷. record를 구별
- candidate key
- NOT NULL
CREATE TABLE instructor( ID CHAR(5), name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, dept_name VARCHAR(20), salary NUMERIC(8,2), PRIMARY KEY (ID), FOREIGN KEY (dept_name) REFERENCES department);- if, ID is the identifier in this column
- ID should not have null values
- ID should not have duplicates in the column
- PRIMARY KEY (A1, ... , An)
Declaring Keys
- An attribute or list of attributes may be declared as PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE
- no two tuples of the relation may agree in all the attribute(s) on the list
- the attributes do not allow duplicates in value
- PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUE can be used as an identifier for each row
- primary key; unique하게 동작, null을 받지않음. relation당 하나의 pk, clustered index
- unique; pk가 아님, null도 받을 수 있음. 하나 이상의 unique를 받을 수 있음, non-clustered index, candidate key
- no two tuples of the relation may agree in all the attribute(s) on the list

- short notification

- 여러 개를 가지고 PK를 선언할 때에는 short not사용하지 않음.

Table Updates (Updating Table Schemas)
- DROP TABLE
- DROP TABLE r
- remove relation r
- 테이블 자체를 지운다.
- DROP TABLE r
- ALTER
- ALTER TABLE r ADD A D
- A라는 이름의 D를 추가한다.
- A is the name of the new attribute to add relation r; D is the domain of A
- All existing tuples in the relation are assigned null as the value for the new attribute
- ALTER TABLE r DROP A
- A는 r안에 있는 attribute의 이름이다.
- Dropping of attributes not supported by many databases
- ALTER TABLE r ADD A D
Integrity Constraints Recap
- Primary key, foreign key, and unique (candidate key) can be specified with DDL
- A single or multiple columns can be specified as a key
- Once a set of columns have been declared unique, any duplicate inputs are rejected
- FORIEGN KEY (state) REFERENCES states
NOT NULL
- disallowing null values
- null → not known → cause problems
- PK는 null이 들어오는 것을 막음.
- NULL? null이 들어와도 상관없음.
- It's DBMS's role to evaluate/ accept/ reject queries
DEFAULT
- default value can be inserted in any column with this keyword
- genre VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'COMEDY'
- 초기값으로 코미디를 할당한다.
- CHECK genre IN ('Comedy', 'Action', 'Drama')
CHECK
- allows the inserted value to be checked
- 애초에 만들때부터 확인하고 넣는 작업.
- INTEGER CHECK (budget > 50000)
- CHECK(release_date BETWEEN '01-Jan-2000' AND '31-DEC-2009'
- 데이터의 범위를 정해준다.
- a column (a) that also can distinguish records in an table

- You are naming the last CHECK constraints as 'release_date_const'
'Lecture Note > [DB] Database Theory' 카테고리의 다른 글
| E-R model (2) | 2023.10.27 |
|---|---|
| Handshaking with an R-DBMS (0) | 2023.10.27 |
| MySQL과 명령어 (0) | 2023.10.27 |
| Relational Algebra (0) | 2023.10.26 |
| Database Systems (0) | 2023.10.26 |


